What Happened As A Result Of Climate Change In North America At The Beginning Of The Archaic Era?
What are the effects of global warming?

Global warming, the gradual heating of Earth's surface, oceans and atmosphere, is caused by man activity, primarily the called-for of fossil fuels that pump carbon dioxide (CO2), methyl hydride and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Already, the consequences and effects of global warming are measurable and visible on the planet.
"Nosotros can observe this happening in real time in many places," Josef Werne, a professor of geology and ecology science at the University of Pittsburgh, told Live Science. "Water ice is melting in both polar ice caps and mountain glaciers. Lakes effectually the globe, including Lake Superior, are warming rapidly — in some cases faster than the surrounding environment. Animals are irresolute migration patterns and plants are changing the dates of action," such as copse budding their leaves earlier in the jump and dropping them later in the autumn.
Hither is an in-depth look at the ongoing furnishings of global warming.
Global warming increases average temperatures and temperature extremes
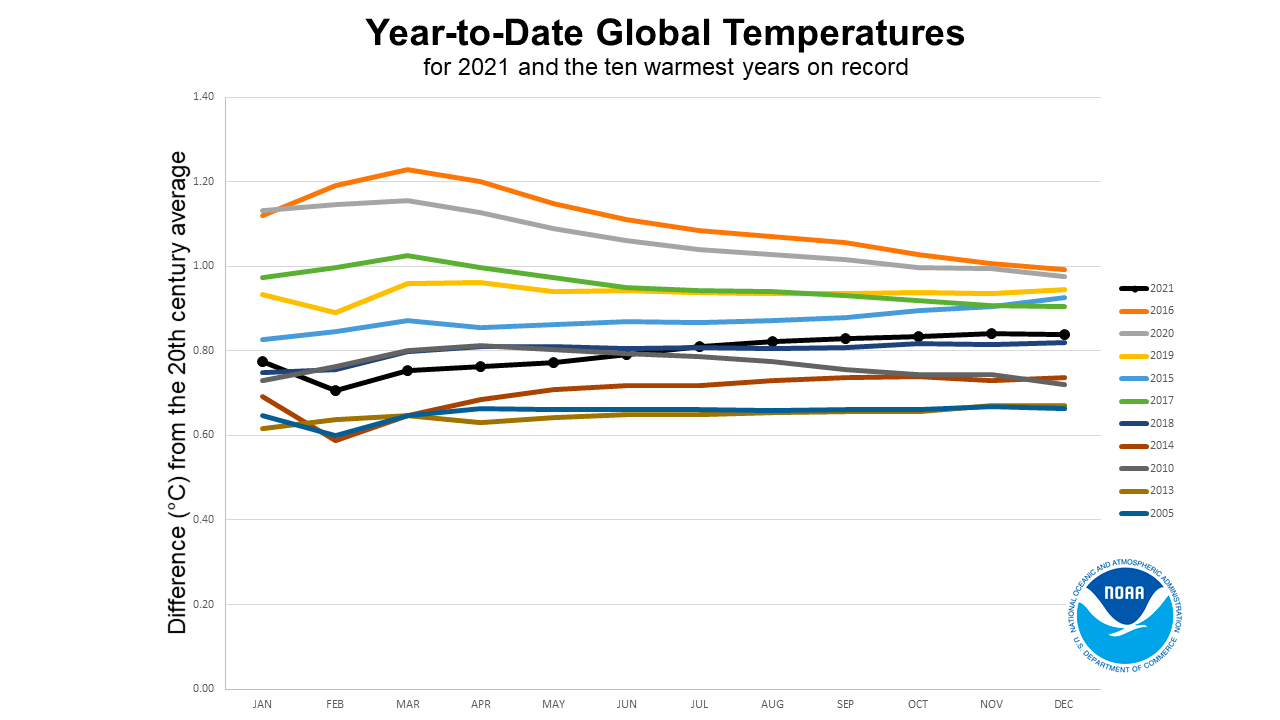
I of the most firsthand and obvious consequences of global warming is the increase in temperatures around the world. The average global temperature has increased by almost i.iv degrees Fahrenheit (0.8 degrees Celsius) over the past 100 years, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
Since record keeping began in 1895, the hottest year on record worldwide was 2016, according to NOAA and NASA information. That year Earth's surface temperature was 1.78 degrees F (0.99 degrees C) warmer than the boilerplate across the entire 20th century. Before 2016, 2015 was the warmest year on record, globally. And before 2015? Yes, 2014. In fact, all 10 of the warmest years on record have occurred since 2005, which tied with 2013 as the 10th-warmest year on tape, co-ordinate to NOAA'due south Global Climate Study 2021. Rounding out the pinnacle vi hottest years on record beyond the earth are (in order of hottest to not as hot): 2020, 2019, 2015, 2017 and 2021.
For the contiguous The states and Alaska, 2016 was the second-warmest yr on record and the 20th sequent year that the annual boilerplate surface temperature exceeded the 122-year average since record keeping began, according to NOAA. Shattered heat records in the U.S. are increasingly becoming the norm: June 2021, for example, saw the warmest temperatures on tape for that month for xv.2%of the contiguous U.Southward. That's the largest extent of tape warm temperatures always recorded in the country, according to the National Centers for Environmental Information.
Global warming increases extreme weather events
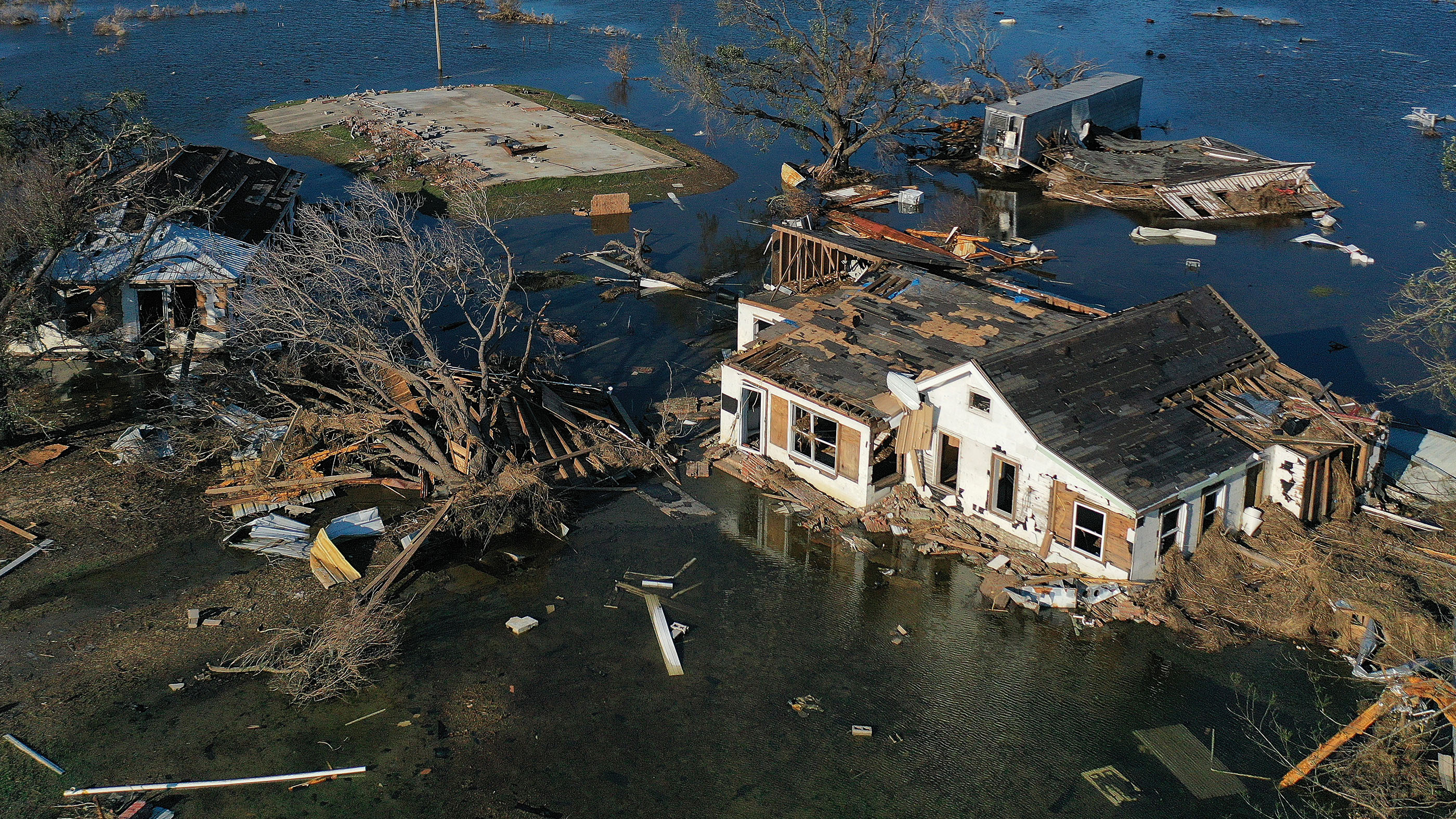

As global average temperatures warm, weather condition patterns are changing. An firsthand consequence of global warming is farthermost weather.
These extremes come in a lot of different flavors. Paradoxically, one event of climatic change can be colder-than-normal winters in some areas.
Changes in climate tin cause the polar jet stream — the boundary between the common cold North Pole air and the warm equatorial air — to migrate s, bringing with it cold, Chill air. This is why some states can take a sudden cold snap or colder-than-normal winter, even during the long-term tendency of global warming, Werne explained.
"Climate is, by definition, the long-term boilerplate of weather, over many years. One cold (or warm) year or season has lilliputian to exercise with overall climate. It is when those common cold (or warm) years go more and more regular that nosotros starting time to recognize it equally a change in climate rather than simply an dissonant yr of weather," he said.
Global warming is too changing other extreme weather. According to the Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory of NOAA, hurricanes are likely to become more than intense, on average, in a warming world. Most computer models propose that hurricane frequency will stay almost the same (or even subtract), only those storms that do course will have the capacity to drop more pelting due to the fact that warmer air holds more wet.
"And even if they become less frequent globally, hurricanes could even so become more frequent in some particular areas," said atmospheric scientist Adam Sobel, author of "Storm Surge: Hurricane Sandy, Our Changing Climate, and Extreme Conditions of the Past and Future" (HarperWave, 2014). "Additionally, scientists are confident that hurricanes will go more intense due to climate modify." This is because hurricanes get their energy from the temperature deviation between the warm tropical ocean and the cold upper temper. Global warming increases that temperature divergence.
"Since the nigh damage past far comes from the most intense hurricanes — such as typhoon Haiyan in the Philippines in 2013 — this ways that hurricanes could go overall more than subversive," said Sobel, a Columbia University professor in the departments of Earth and Environmental Sciences, and Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics. (Hurricanes are called typhoons in the western N Pacific, and they're called cyclones in the South Pacific and Indian oceans.)
What's more, hurricanes of the future will be hitting shorelines that are already decumbent to flooding due to the ocean-level rise caused by climate modify. This means that any given storm will likely cause more damage than it would have in a globe without global warming.
Lightning is another weather feature that is being affected by global warming. Co-ordinate to a 2014 study, a 50% increment in the number of lightning strikes within the United States is expected by 2100 if global temperatures continue to ascent. The researchers of the study found a 12% increase in lightning activeness for every 1.viii degree F (1 caste C) of warming in the atmosphere.
NOAA established the U.Southward. Climate Extremes Index (CEI) in 1996 to track extreme weather events. The number of extreme conditions events that are among the almost unusual in the historical record, according to the CEI, has been rise over the concluding iv decades.
Scientists project that farthermost weather events, such as oestrus waves, droughts, blizzards and rainstorms will continue to occur more than frequently and with greater intensity due to global warming, according to Climate Central. Climate models forecast that global warming will cause climate patterns worldwide to experience significant changes. These changes volition probable include major shifts in air current patterns, annual precipitation and seasonal temperatures variations. These impacts vary by location and geography. For case, according to the U.S. Ecology Protection Agency (EPA), the eastern United States has been trending wetter over time, while the Westward – and particularly the Southwest – accept become increasingly dry.
Because loftier levels of greenhouse gases are likely to remain in the atmosphere for many years, these changes are expected to last for several decades or longer, co-ordinate to the EPA.
Global warming melts ice
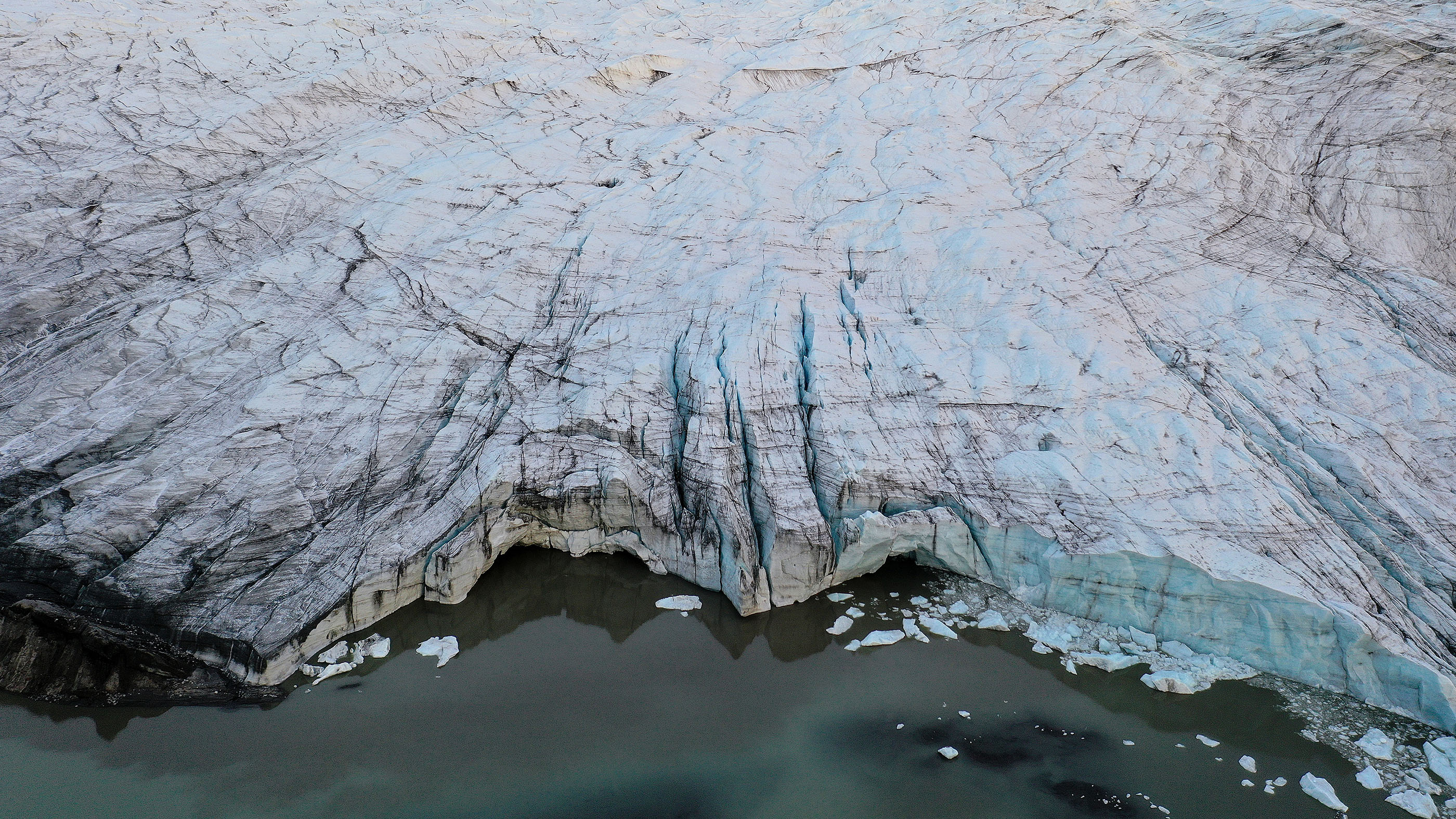

1 of the master manifestations of climatic change and then far is melt. Due north America, Europe and Asia accept all seen a trend toward less snow cover between 1960 and 2015, according to 2016 research published in the periodical Current Climate Change Reports. Co-ordinate to the National Snow and Water ice Data Center, in that location is now x% less permafrost, or permanently frozen ground, in the Northern Hemisphere than at that place was in the early 1900s. The thawing of permafrost can cause landslides and other sudden land collapses. It tin can also release long-buried microbes, every bit in a 2016 case when a cache of buried reindeer carcasses thawed and caused an outbreak of anthrax.
Ane of the virtually dramatic effects of global warming is the reduction in Arctic sea ice. Sea water ice hit record-depression extents in both the fall and winter of 2015 and 2016, pregnant that at the time when the ice is supposed to be at its peak, it was lagging. The melt means there is less thick body of water ice that persists for multiple years. That ways less heat is reflected back into the atmosphere by the shiny surface of the ice and more is captivated by the insufficiently darker ocean, creating a feedback loop that causes even more melt, co-ordinate to NASA'south Operation IceBridge.
Glacial retreat, too, is an obvious upshot of global warming. Only 25 glaciers bigger than 25 acres are now constitute in Montana'south Glacier National Park, where most 150 glaciers were once found, according to the U.S. Geological Survey. A like tendency is seen in glacial areas worldwide. According to a 2016 report in the journal Nature Geoscience, there is a 99% likelihood that this rapid retreat is due to human-caused climate change. Some glaciers retreated up to 15 times every bit much as they would take without global warming, those researchers found.
Sea levels and bounding main acidification
In general, equally ice melts, sea levels ascent. According to a 2021 report by the World Meteorological Organization, the footstep of sea level rise doubled from 0.08 inches (2.1 millimeters) per year between 1993 and 2002 to 0.17 inches (iv.4 mm) per yr betwixt 2013 and 2021.
Melting polar water ice in the Arctic and Antarctic regions, coupled with melting ice sheets and glaciers across Greenland, North America, Due south America, Europe and Asia, are expected to raise sea levels significantly. Global sea levels have risen most 8 inches since 1870, co-ordinate to the EPA, and the charge per unit of increment is expected to accelerate in the coming years. If current trends go along, many coastal areas, where roughly one-half of the Earth's human population lives, will be inundated.
Researchers projection that by 2100, average ocean levels will be 2.3 anxiety (.vii meters) higher in New York City, ii.9 feet (0.88 m) higher at Hampton Roads, Virginia, and 3.5 feet (1.06 m) college at Galveston, Texas, the EPA reports. According to an IPCC report, if greenhouse gas emissions remain unchecked, global sea levels could rise by as much as 3 feet (0.ix meters) past 2100. That estimate is an increase from the estimated 0.9 to 2.7 feet (0.3 to 0.8 meters) that was predicted in the 2007 IPCC report for future ocean-level rise.
Body of water level isn't the merely thing changing for the oceans due to global warming. As levels of CO2 increase, the oceans blot some of that gas, which increases the acidity of seawater. Werne explains it this style: "When you dissolved CO2 in h2o, y'all get carbonic acid. This is the aforementioned exact affair that happens in cans of soda. When you pop the height on a can of Dr Pepper, the pH is 2 — quite acidic."
Since the Industrial Revolution began in the early 1700s, the acidity of the oceans has increased almost 25 per centum, according to the EPA. "This is a problem in the oceans, in large function, because many marine organisms make shells out of calcium carbonate (call up corals, oysters), and their shells dissolve in acid solution," said Werne. "So as we add more and more CO2 to the ocean, it gets more than and more acidic, dissolving more and more shells of bounding main creatures. Information technology goes without saying that this is not good for their health."
If current ocean acidification trends keep, coral reefs are expected to become increasingly rare in areas where they are now common, including nigh U.S. waters, the EPA reports. In 2016 and 2017, portions of the Great Barrier Reef in Australia were hitting with bleaching, a miracle in which coral eject their symbiotic algae. Bleaching is a sign of stress from too-warm waters, unbalanced pH or pollution; coral tin recover from bleaching, but back-to-back episodes brand recovery less likely.
Plants and animals
The effects of global warming on the Earth's ecosystems are expected to be profound and widespread. Many species of plants and animals are already moving their range northward or to higher altitudes as a result of warming temperatures, co-ordinate to a study from the National Academy of Sciences.
"They are non just moving northward, they are moving from the equator toward the poles. They are quite simply post-obit the range of comfy temperatures, which is migrating to the poles equally the global average temperature warms," Werne said. Ultimately, he said, this becomes a problem when the charge per unit of climate change velocity (how fast a region changes put into a spatial term) is faster than the rate that many organisms can migrate. Considering of this, many animals may not be able to compete in the new climate authorities and may go extinct.
Additionally, migratory birds and insects are now arriving in their summer feeding and nesting grounds several days or weeks earlier than they did in the 20th century, according to the EPA.
Warmer temperatures will also expand the range of many disease-causing pathogens that were once confined to tropical and subtropical areas, killing off plant and creature species that formerly were protected from disease.
A 2020 study published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences suggested that one in every 3 species of plant and animal are at risk of extinction by 2070 due to climate change.
Social effects
Every bit dramatic as the effects of climate alter are expected to be on the natural world, the projected changes to man society may be even more devastating.
Agricultural systems volition probable be dealt a crippling accident. Though growing seasons in some areas volition aggrandize, the combined impacts of drought, severe conditions, lack of accumulated snowmelt, greater number and variety of pests, lower groundwater tables and a loss of arable land could crusade astringent crop failures and livestock shortages worldwide.
North Carolina Land University besides notes that carbon dioxide is affecting constitute growth. Though CO2 can increase the growth of plants, the plants may become less nutritious.
This loss of nutrient security may, in turn, create havoc in international nutrient markets and could spark famines, nutrient riots, political instability and ceremonious unrest worldwide, according to a number of analyses from sources as diverse every bit the U.S Section of Defence force, the Center for American Progress and the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars.
In addition to less nutritious food, the result of global warming on human being health is also expected to exist serious. The American Medical Association has reported an increment in mosquito-borne diseases like malaria and dengue fever, every bit well equally a rise in cases of chronic conditions like asthma, nigh likely as a direct upshot of global warming. The 2016 outbreak of Zika virus, a mosquito-borne illness, highlighted the dangers of climate change. The disease causes devastating birth defects in fetuses when pregnant women are infected, and climate change could make higher-latitude areas habitable for the mosquitoes that spread the illness, experts said. Longer, hotter summers could also atomic number 82 to the spread of tick-borne illnesses.
Further reading on the impacts of global warming
For more on the potential impacts of climate change in urban environments, the freely available book affiliate Climate Change and its Impacts in the book "Climate Change Resilience in the Urban Environs" (IOP Publishing, 2017) covers the challenges that lay ahead for human populations.
Finally, for a psychological deep-dive on why all of this bad news is hard to accept in, effort "Don't Even Think Nearly It: Why Our Brains Are Wired to Ignore Climatic change" (Bloomsbury USA, 2015) past climate activist and communicator George Marshall.
Boosted resource
- This NASA page includes a series of visualizations that illustrate how some of Globe's key climate indicators — sea ice, sea level, global temperature and carbon dioxide — are changing over time.
- This NOAA sea-level rise learning module includes educational videos, groundwork for teachers, learning objectives and more.
- ClimateBrief has gathered 10 of the best climate change videos on YouTube.
Bibliography
- EPA: Climatic change: Basic Information
- NASA: Global Climate change
- NOAA: Climate News and Data
Source: https://www.livescience.com/37057-global-warming-effects.html
Posted by: pascodomesed.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Happened As A Result Of Climate Change In North America At The Beginning Of The Archaic Era?"
Post a Comment